Bad programmers worry about the code. Good programmers worry about data structures and their relationships: Data Structures
I have a CS background but understood very little of data structures and algorithms while in school. Maybe I wasn't paying attention or the lecturer didn't do a good job teaching it or its a problem with multidimensional factors, that doesn't matter now. I have taken time to take courses to study and understand data structures and I'll explain using code samples in python.
Data Structure is a way of collecting and organising data in such a way that we can perform operations on these data in an effective way. Data Structures is about rendering data elements in terms of some relationship, for better organization and storage. To really optimize a code, an understanding of data sctructures is needed. And this is what separates code monkeys and effective problem solvers. Coding is more than just tapping on your keyboard based on some unclear requirements, it is the abstraction of the conceptualization of a solution to a problem and to do that effectively, the nitty gritty of how the data should be stored is needed.
Array
Array is a container which can hold a fix number of items and these items should be of the same type. An element refers to each item contained in an array, an index refers to the location of an element.
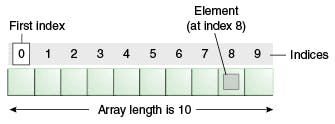
Operations time complexities
Insert at the end: constant O(1)
Insert at the begining: linear O(n)
Insert generally: linear O(n)
Remove from end: constant O(1)
Remove from begining: linear O(n)
Remove generally: linear O(n)
Find value: linear O(n)
Access value: constant O(1)
Linked List
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers. The difference between this and an array is that an array stores elements in contigous memory while linked list doesn't. This means that elements in an array can be accessed faster using the index, but for a linked list, an element also contains information on the next element. There are 3 types of linked list: singly linked list, doubly linked list, circular linked list but in this article we will be dealing with singly linked list only.
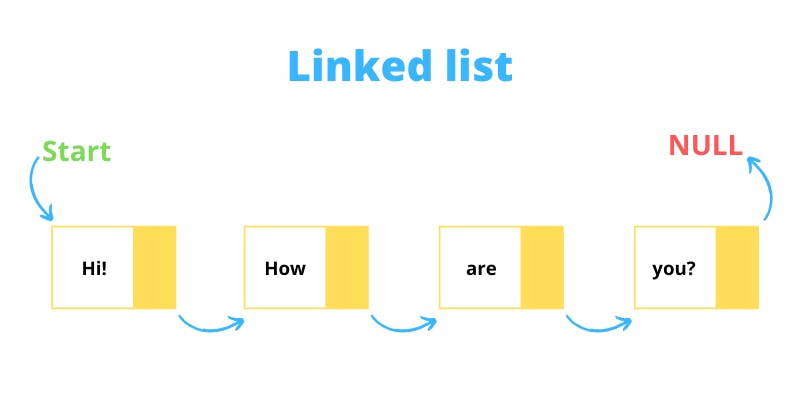
Operations time complexities
Insert at the end: constant (if you have a reference to the next node)
Insert at the begining: constant
Insert generally: linear (if you don't have a reference to the next node)
remove generally: linear
Find value: linear
Access value: linear
HashTable
In a hash table, data is stored like a table, a key and an element the key is pointing to. The difference between this and an array is that in an array, the indexes are integers and ordered but in a hash table, the key could be of any type and there's no order to it.
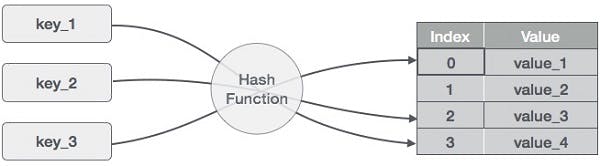
Operations time complexities
Insertion: linear O(n)
Remove: linear O(n)
Find value: linear O(n)
Stack
A stack is a LIFO (Last In, First Out) data structure. Elements are added or removed at the top of the stack with the last item to the pushed (added) to the stack to be first to be popped (removed)
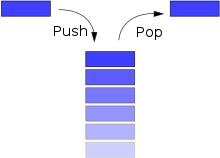
Operations time complexities
Insert at the end: constant
Insert at the begining: not available
Insert generally: constant
Remove from end: constant
Remove from begining: not available
Find value: linear
Access value: linear(if the underlying structure is a linked list) constant (if the underlying structure is a array)
Queue
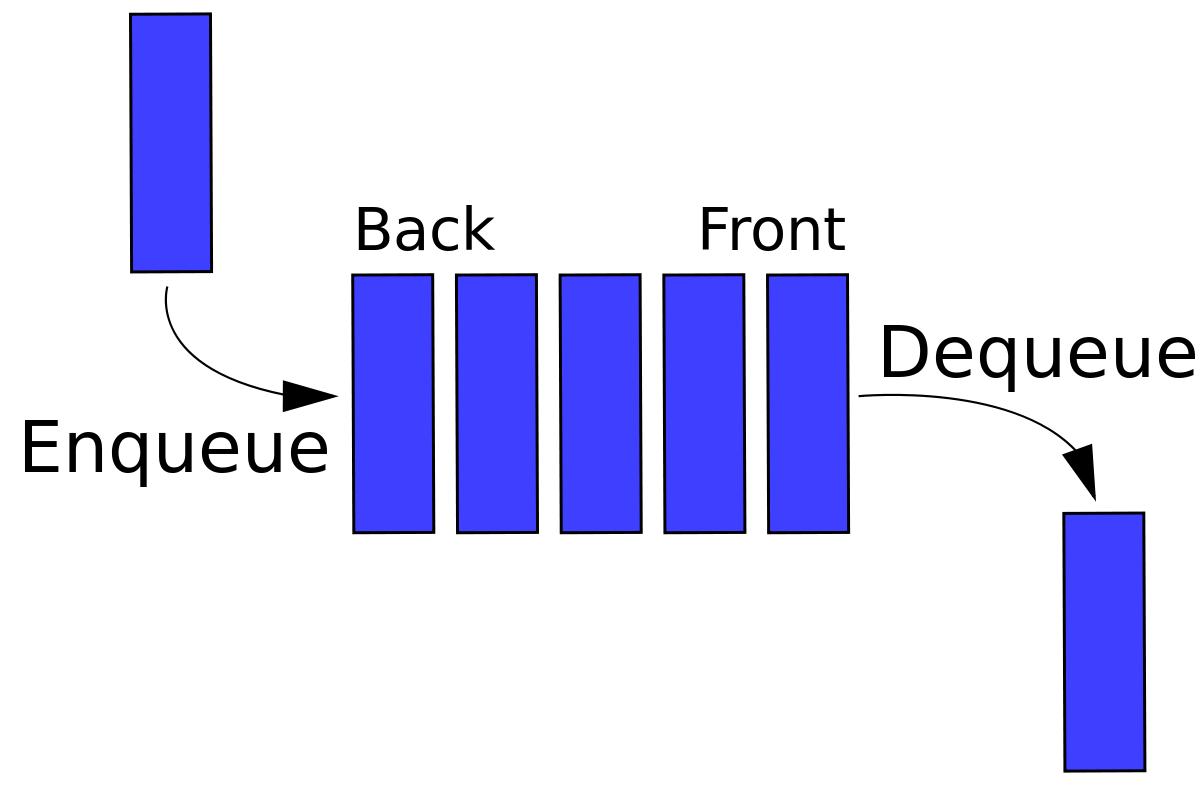
Operations time complexities
Insert at the end: not available
Insert at the begining: linear (array)
Insert generally: constant (linked list)
Remove from end: not available
Remove from begining: linear (array) constant (linked list)
Fnd value: linear
Access value: linear(linked list) constant (array)
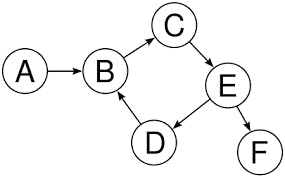
Graph
A graph G consists of two types of elements: vertices and edges. Each edge has two endpoints, which belong to the vertex set. We say that the edge connects (or joins) these two vertices.
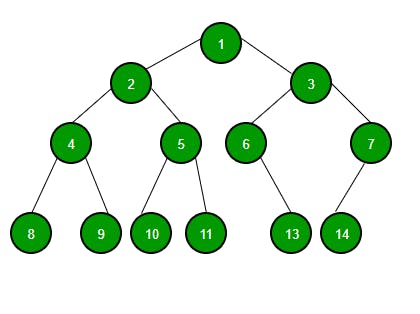
Tree
A tree is a collection of entities called nodes. Nodes are connected by edges. Each node contains a value or data, and it may or may not have a child node .
Operations time complexities
Search: linear
Insertion: linear
Deletion: linear
