Introduction
In the previous article, I explained proxy servers and how they work, since we have understood the storage and exchange of data on a network, I will explain how that process can be made faster, more secure and resilient- web caching.
Goal
By the end of this article you should be able to understand what is caching and when to use it.
Let's delve in
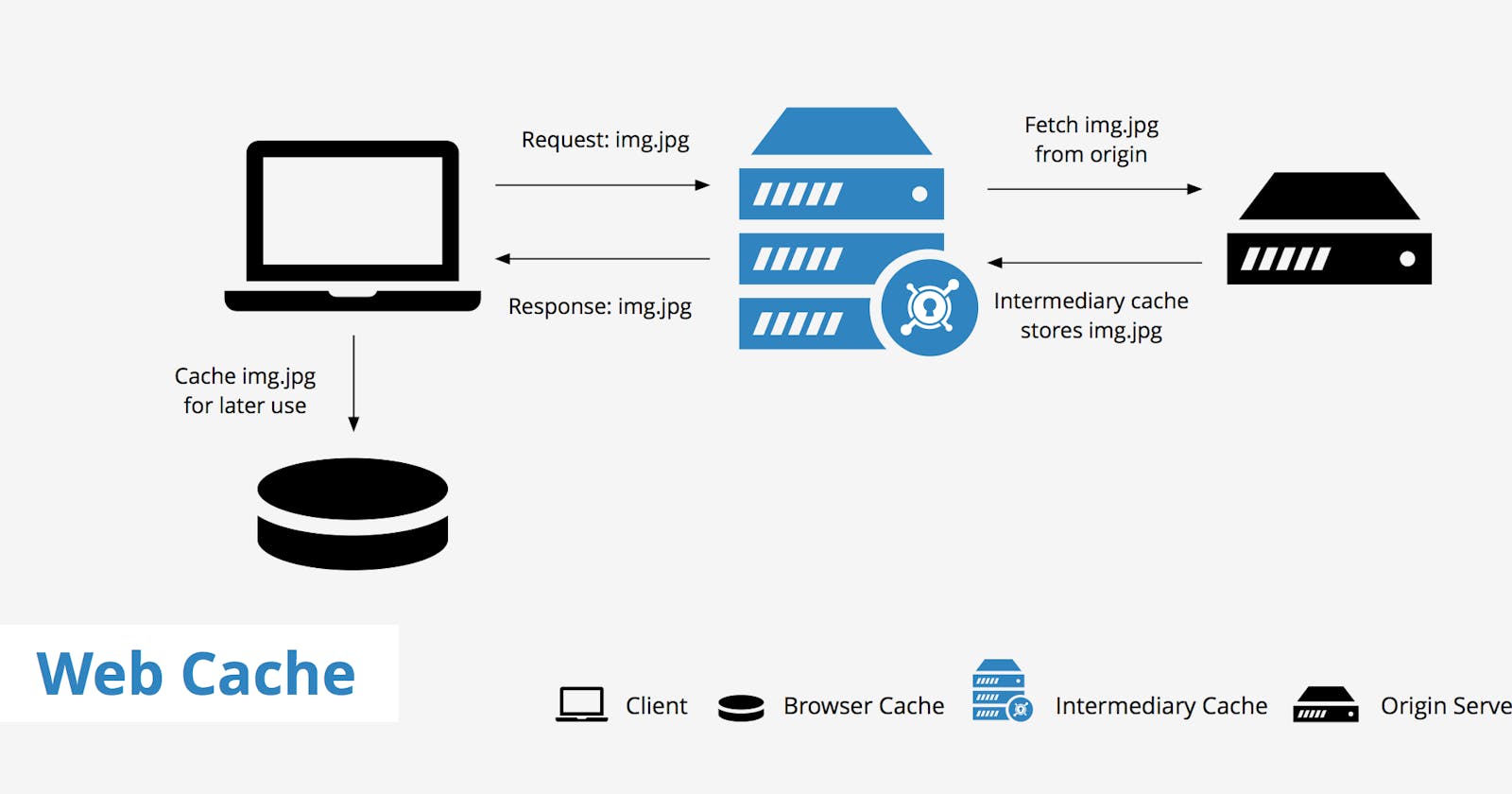
Web Caching
Web caching is the technique of storing data from a web server for reuse, such as a copy of a web page.
Cached data is data stored the first time a user visits a webpage. The next time a user requests the same page, a cache will serve the copy, which helps keep the origin server from getting overloaded and also reduce the request-response lifecycle.
Web caching solutions and strategies enhance page delivery speed significantly and reduce the work needed to be done by the backend server.
Caching can also protect against total outages, delivering already cached content when servers are down.
Reasons for caching
Ranking: faster websites are more favored by search engines and hence they will rank higher
Increased performance: When some responses are stored in the cache, the main web server will have more resources to perform other tasks efficiently
Decreased network costs: The time required for a request-response lifecycle to complete between a user and the web server will be reduced when the data is cached
Some caching solutions
What's next
Now that we understand how information are stored on web servers and cache, I will explain Message queue.